The following is a random list I’ve aggregated of some interesting stuff that should remove a bit of fear, increase optimism, and in a way make you more malleable/flexible for the change that is to come.
I love you all, and I don’t want to see anyone caught off guard in this beautiful life; bad things happen, but so do great things:
The Printing Press and its Impact:
Johannes Gensfleisch zur Laden zum Gutenberg invented the printing press in 1440.
Within 50 years, there were 1,000 printing presses around Europe.
Before the press, manuscript production in the Middle Ages reached hundreds of thousands per major country per century.
By the 17th century, Europe's book production reached 500 million.
The introduction of the printing press caused a 340-fold decrease in the price of books.
Early Mechanical Computers and AI Speculation:
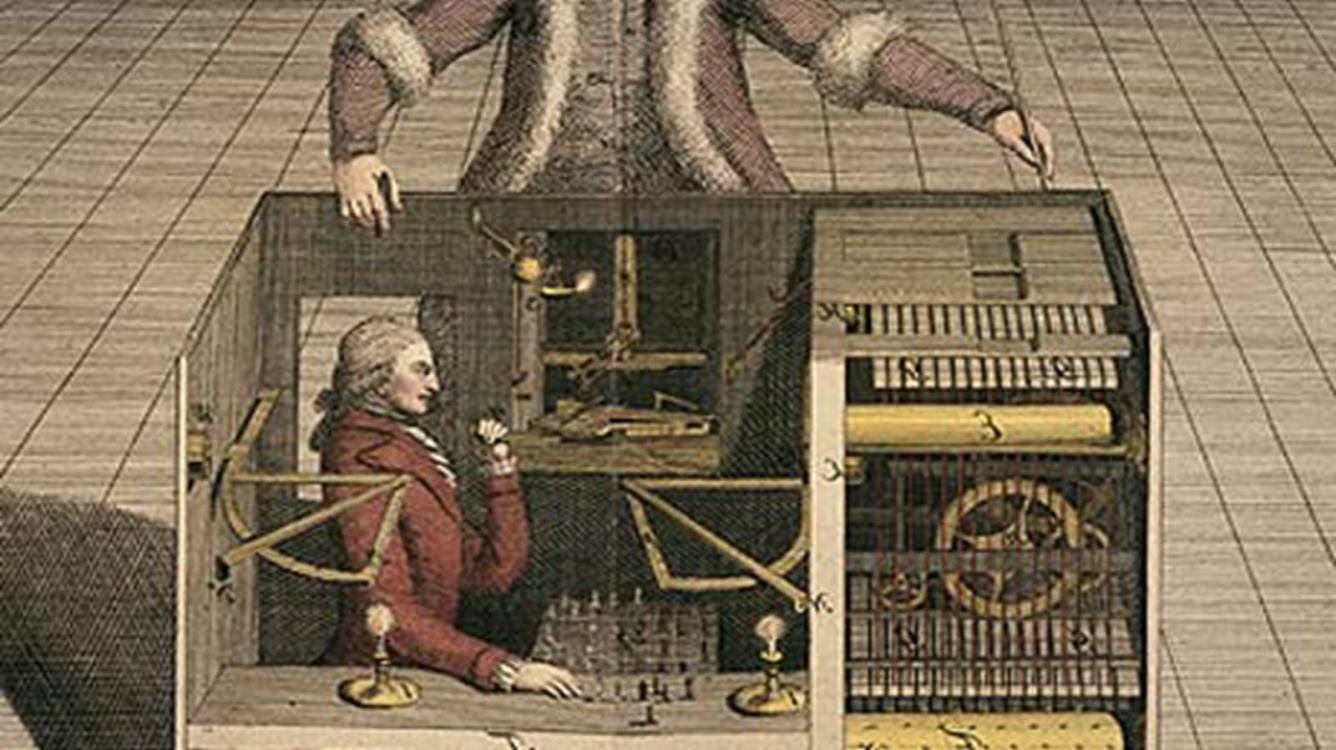
6. In 1770, the invention of the first mechanical chess computer stunned those who saw it—a chessboard set upon an elaborate cabinet, with its chess pieces manipulated by a robot dressed as an Ottoman wizard.
It toured the world from 1770 to 1838.
The machine, also known as the Mechanical Turk, beat Benjamin Franklin and Napoleon in chess matches and led Edgar Allan and Poe to speculate on the possibility of artificial intelligence upon seeing it in the 1830s.
It was all a lie, of course—the machine cleverly hid a real chess master inside its fake gears, but our ability to believe that machines might be able to think fooled many of the best minds in the world for three quarters of a century.
Telephone and Early Electricity:
10. Alexander Graham Bell introduced the telephone in 1876.
The first electricity power stations were introduced in London and New York in 1882.
By 1900, 2% of fossil fuel production was dedicated to generating electricity, increasing to over 10% by 1950 and exceeding 30% by 2000.
By 1900, America had 600,000 telephones, and this number rose to 5.8 million by 1910.
Development of Early Computers and Electronics:
14. In the 1940s, Britain’s Bletchley Park began developing a true computer. (Shoutout Turing)
ENIAC, a precursor to modern computers, was developed by the University of Pennsylvania in 1945.
In 1947, Bell Labs introduced the transistor. (Shoutout Shockley, Bardain, and Brattain)
Technological Adoption and Advancement:
17. A TV that cost $1000 in 1950 would cost around $8 in 2023.
First Machine Learning: Fast-forward to 1950, when a toy and a thought experiment, each developed by a different genius of the still-developing field of computer science, led to a new conception of artificial intelligence. The toy was a jury-rigged mechanical mouse called Theseus, developed by Claude Shannon, an inventor, prankster, and the greatest information theorist of the twentieth century. In a 1950 film, he revealed that Theseus, powered by repurposed telephone switches, could navigate through a complex maze—the first real example of machine learning.
Wide Spread adoption of a tech is usually slow: The internet is a great example. While it was born as ARPANET in the late 1960's, it took nearly three decades to achieve general use in the 1960s, with the invention of the web browser, the development of affordable computers, and the growing infrastructure to support high-speed internet. It was fifty years before smartphones enabled the rise of social media. And many companies have not fully embraced the internet: making a business 'digital' is still a hot topic of discussion at business school, especially as many banks still use mainframe computers. And previous General Purpose Technologies have similarly taken many decades from development until they were useful. Consider computers, another transformative Technology. Early computers improved quickly, thanks to Moore's law, the long-standing trend that the capability of computers doubles every two years. But it still took decades for computers to start appearing at businesses and schools because, even with their fast rate of increasing ability, they were starting from a very primitive beginning. Yet LLMs proved incredibly capable within a few years of their invention. They've also been adopted by consumers very quickly; chatgpt reached 100 million users faster than any previous product in history, driven by the fact that it was free to access, available to individuals, and incredibly useful.
Recent Advances and Impacts:
20. Oppenheimer regretted the unstoppable nature of atomic bombs once created.
The introduction of refrigerators using CFCs led to ozone layer damage.
Internal combustion engines contributed to global warming.
Overuse of antibiotics has led to stronger, more resistant bacteria strains.
Satellites have created "space junk," complicating space flight.
In 2022, a significant breakthrough in nuclear fusion demonstrated net energy gain.
Geopolitical and Technological Strategies: In his 2022 address, Xi Jinping emphasized China’s focus on science and technology as the primary resources for strategic national needs.
\( @ pEnTaGonn C411 M3 if s3ri0us\)
Resistance to Technology:
27. The Ottoman Empire resisted the printing press as a Western innovation for nearly three centuries.
Pope Urban II in medieval times wanted to ban the crossbow.
Queen Elizabeth I temporarily banned certain knitting machines.
The Tokugawa shogunate in Japan isolated the country from foreign technology for 300 years.
China rejected British offers of Western technology in the late 18th century under Emperor Qianlong.
Technologies That Faded but Impacted Future Innovations:
32. Nintendo DS has been replaced by newer technologies like the Nintendo Switch.
Typewriters have been replaced by digital solutions like Google Docs.
Impact of Large Language Models (LLMs):
34. LLMs are trained on trillions of words, far exceeding the average human's annual reading volume.
Technological Augmentation:
35. GitHub Copilot enhances coding speed by 55%.
Electrodes implanted in an ALS patient enabled communication.
Successful Adoption of Technology: 37. John Deere's invention of a steel plow catalyzed the growth of his company and agricultural technology.
Improvements in Efficiency: 38. Solar energy costs decreased from $4.88/watt in 2000 to $0.38/watt.